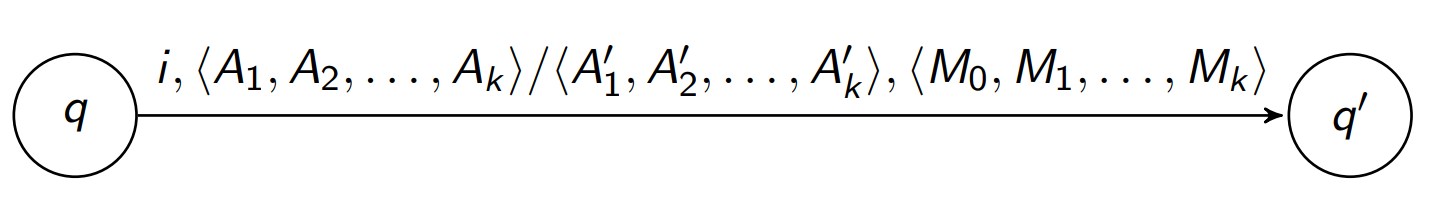Lab Session #7
#
Agenda
#
- Turing Machine
- Formal definition
- Example
- Exercices
Turing Machine
#
A Turing Machine (TM) with k-tapes is a tuple
T=⟨Q,I,Γ,δ,q0,Z0,F⟩where:
Q
is a finite set of states;
I
is the input language;
Γ
is the memory alphabet;
δ
is the transition function;
q0∈Q
is the initial state;
Z0∈Γ
is the initial memory symbol;
F⊆Q
is the set of final states.
Transition Function
#
The transition function is defined as
δ:(Q−F)×(I∪{_})×(Γ∪{_})k→Q×(Γ∪{_})k×{R,L,S}k+1where elements of {R,L,S}
indicate “directions” of the head of the TM:
Remarks:
the transition function can be partial;
the transition function can be partial;
the transition function can be partial;
Moves
#
Moves are based on
one symbol read from the input tape,
k symbols, one for each memory tape,
state of the control device.
Actions
Moves: Graphically
#
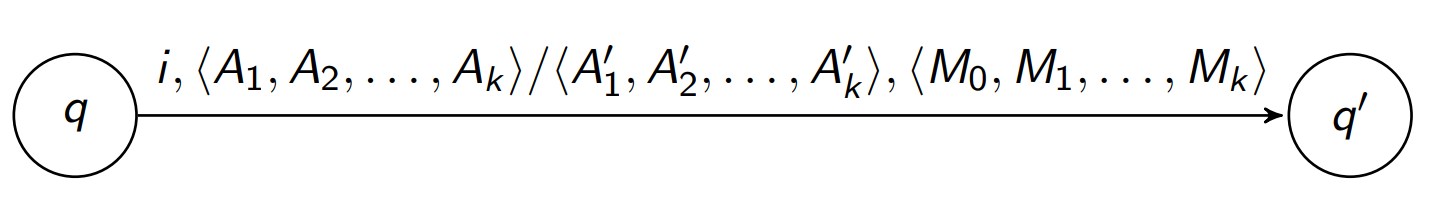
q∈Q−F
and q′∈Q
i
is the input symbol,
Aj
is the symbol read from the jth
memory tape,
A′j
is the symbol replacing Aj
,
M0
is the direction of the head of the input tape,
Mj
is the direction of the head of the jth
memory tape.where 1≤j≤k
Configuration
#
A configuration (a snapshot) c
of a TM with k
memory tapes is
the following (k+2)
-tuple:
c=⟨q,x↑y,α1↑β1,...,αk↑βk⟩where:
- q∈Q
- x∈(I∪{_})∗,y=y′._
with y′∈I∗
- αr∈(Γ∪{_})∗
and βr′=βr′._
with βr′∈Γ∗
and 1≤r≤k
- ↑∈/I∪Γ
Acceptance Condition
#
If T=⟨Q,I,Γ,δ,q0,Z0,F⟩
is a TM and s∈I∗,s
is accepted by T
if c0⊢∗cF
where:
c0
is an initial configuration defined as c0=⟨q0,↑s,↑Z0,...,↑Z0⟩
where
- x=ϵ
- y=s_
- αr=ϵ,βr=Z0
, for any 1≤r≤k.
cF
is a final configuration defined as cF=⟨q,s′↑y,α1↑β1,...,αk↑βk⟩
where
- q∈F
- x=s′
L(T)={s∈I∗∣x
is accepted by T}
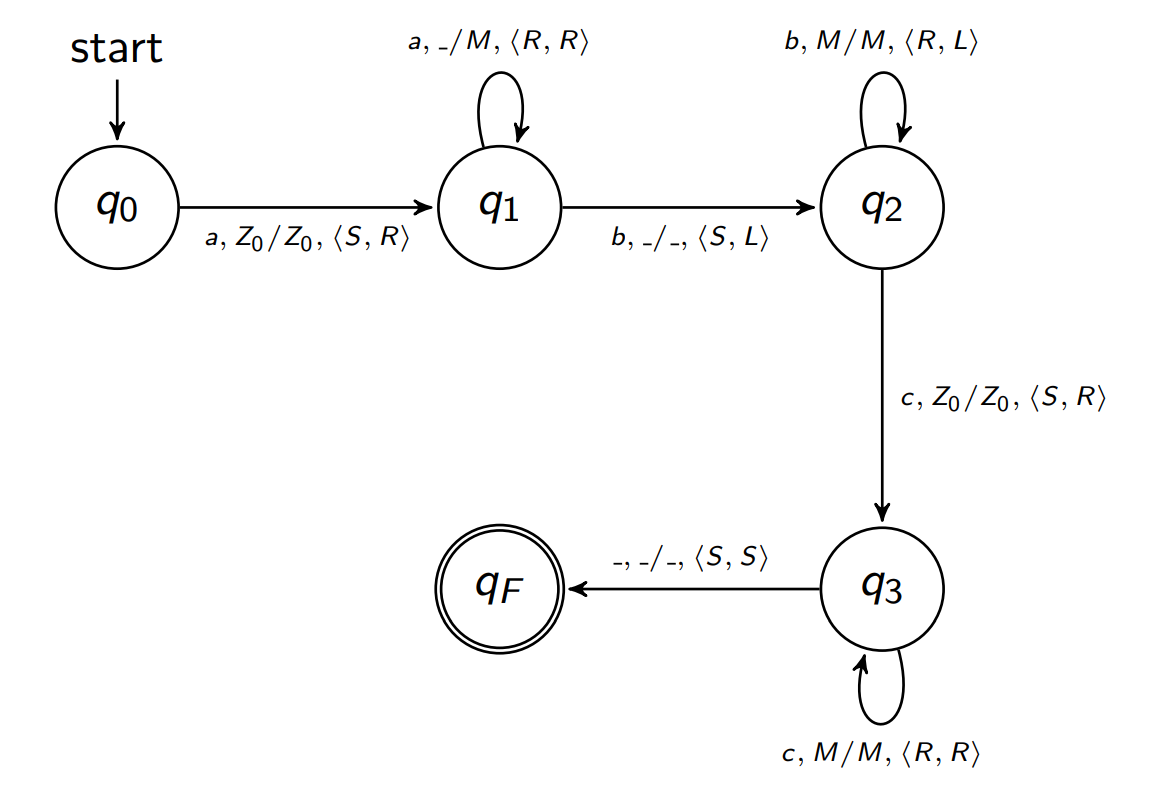
Example
#
A TM T
that recognises the language AnBnCn={anbncn∣n>0}
Exercices
#
Build TMs that recognise the following languages:
- L1={wcw∣w∈{a,b}+}
- L2={wcwR∣w∈{a,b}+}
, where wR
is the reversed string w
.
- L3={w∣w∈{a,b}∗}
, where w
is a palindrome.
- L4={anbn∣n≥0}∪{anb2n∣n≥0}
Solutions:
Homework Exercices
#
Build TMs that recognise the following languages:
- L5={(ab)n,n≥0}
- L6={anb2nc3n,n≥0}